Data Collection & Telemetry
Overview
Update Hardware
Module and SIM Update Guides
Module Identification
Module Swap Wizard
SIM Swap Wizard
AT&T / T-Mobile Configuration Guide
Verizon Configuration Guide
Worldwide H1 SIM Configuration Guide
SIM Replacement Instructions
Wi-Fi Configuration Guide
Firmware Update
Troubleshoot
ZL6 Troubleshooting Guide
ATMOS 41W Troubleshooting Guide
EM60G Troubleshooting Guide
EM50 Series Troubleshooting Guide
Communication Test
List Cellular Carriers
Test Button & Status Lights
Fix: Retroactively Enable LTE-M Bands for 4G in Europe
Sensor Current Draw Check - ZSC
App Location Permissions on iOS and Android
Coverage
Accessories
ZENTRA Cloud 1.0
Quick Start
Organizations
Account
Edit Account Profile
Update Account Password
Lost Password/Password Reset
Set Measurement Unit Preferences
Users
Devices
Device Inventory
Edit Device
Re-provision ZL6 to European Server
Add Device
Remove Device
Time-zone and Location Override
Calibrations
Downloads
Dashboard
Enable Chart Status
Create Custom Charts
Color Picklist
Add Traces to Chart
Chart Stats
Print Charts
Set a Target Range
Lock Chart Axes
Chart Date Range Picker [NEW]
Download Chart Data
Notifications
Models
Daily Light Integral
Ground Water Elevation
Ground Water Depth
Plant Available Water
Daily Light Photoperiod
Chill Hours
Growing Degree Days
Create a Model
Evapotranspiration
Subscriptions
API
US Server API
EU Server API
TAHMO Server API
Push API
R Package
API Troubleshoot
AgWeatherNet & DAS
Manage API Keys
Error Codes
Applications
FAQ
Accessibility
Release Notes
ZENTRA Field
ZENTRA Cloud 2.0
Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction to 2.0
Getting Started
User Account
Setup
Devices
Add Data Logger
Configure Data Logger
Device Map
Data Logger Charts
Download Data Logger
Logs
Archive
Dashboards
Explorer
Data
Projects
Alerts
Environment Models
Chill Hours [2.0]
Daily Light Integral [2.0]
Daily Light Photoperiod [2.0]
Evapotranspiration [2.0]
Groundwater Elevation [2.0]
Groundwater Depth [2.0]
Growing Degree Days [2.0]
Heat Index [2.0]
Heat Stress Wet Bulb Globe Temperature WBGT [2.0]
Leaf Wetness Amount of Water [2.0]
Plant Available Water [2.0]
Utah Chill Model [2.0]
Wind Chill [2.0]
Subscriptions
API
Feedback
Accessibility
ZENTRA Cloud 2.0 Notes
Privacy, Security, Terms & Conditions
Uptime Monitor
- All Categories
- ZENTRA Cloud 1.0
- Models
- Growing Degree Days
Growing Degree Days
The development of plants depends on the accumulation of heat. Accumulated growing degree days (GDDs) can be used to predict when a crop will reach a particular growth stage.

The development of plants depends on the accumulation of heat. Accumulated Growing Degree Days (GDDs) can be used to predict when a crop will reach a particular growth stage.
Two methods are presented by McMaster and Wilhelm (1997). Method 2 is used in the ZENTRA Cloud environmental model for GDD.
Method 2 implements a value check against the maximum (Tx) and minimum (Tn) temperatures before calculating Tavg.
Formula: Tavg = (Tx* + Tn*) / 2
Tx* and Tn* are the adjusted maximum and minimum temperatures.
- If Tx is greater than the upper temperature limit then Tx* is set to equal the upper temperature limit.
- If Tx is smaller than the base temperature then Tx* is set to equal the base temperature.
- If Tn is greater than the upper temperature limit then Tn* is set to equal the upper temperature limit.
- If Tn is smaller than the base temperature then Tn* is set to equal the base temperature.
METER Sensors that support GDD:
GDD
- Click the environmental model icon.
- Select Growing Degree Days.
- Enter a name for the model and a name for the chart.
- Enter values for the Maximum and Minimum(i.e. Base) temperature.
- A default air temperature measurement will be selected. Select a different measurement if desired.
- Optional: Enter the target GDD.
- Click Create.
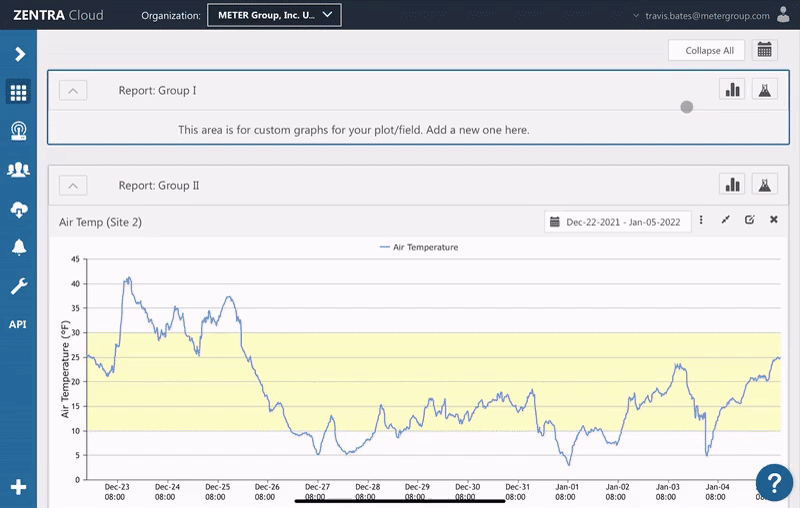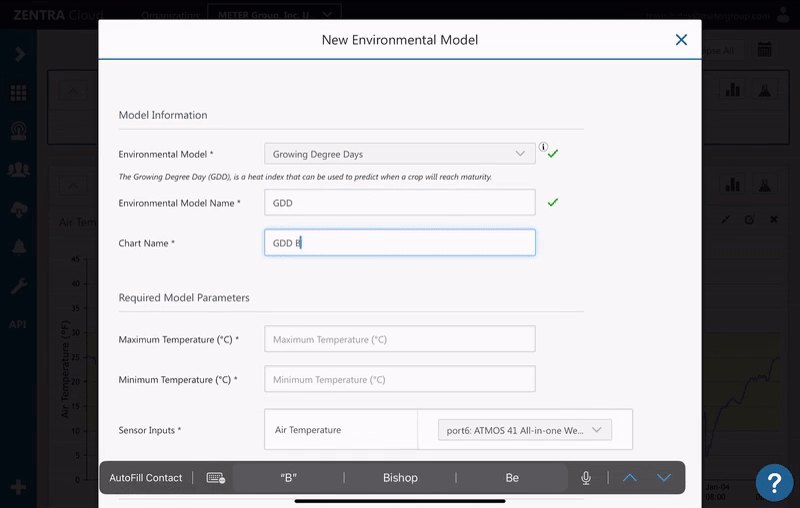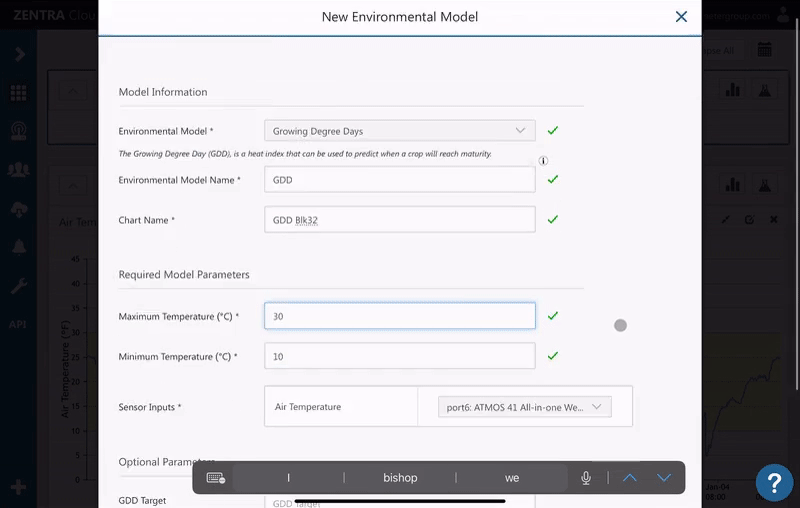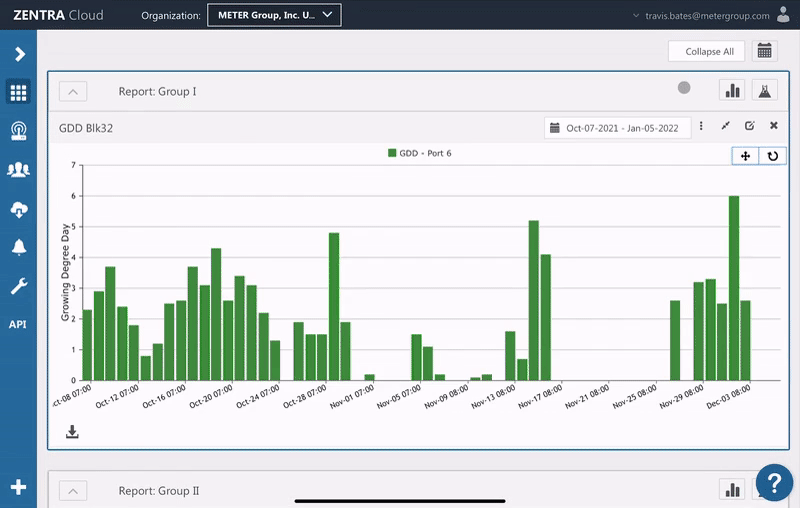
Accumulated GDD
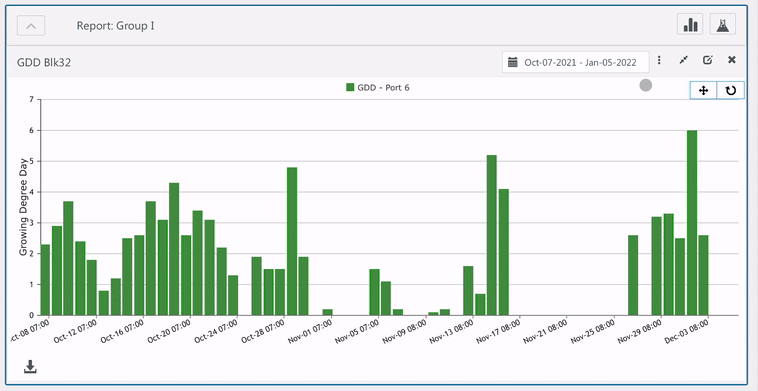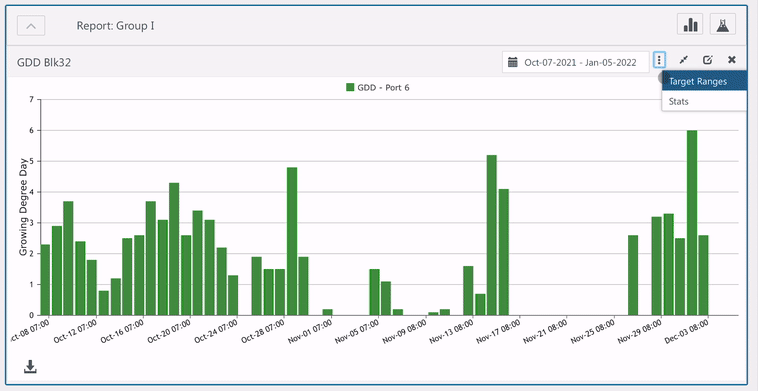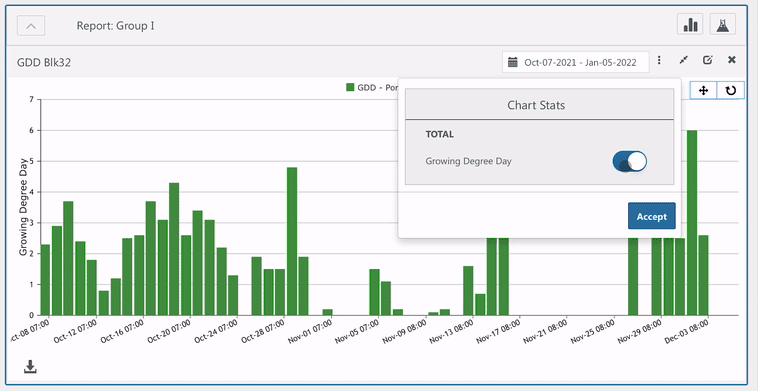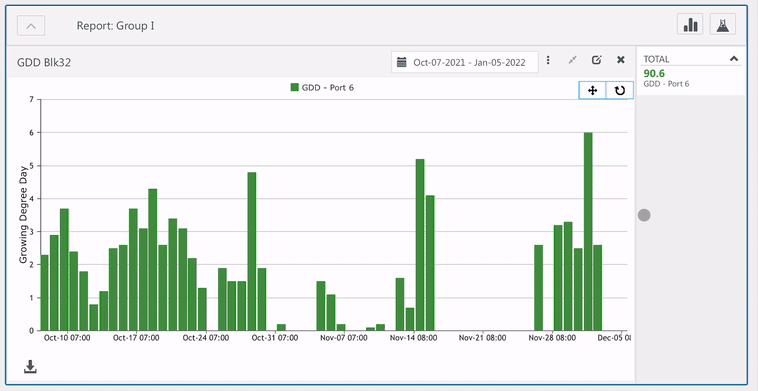
- Click the Vertical Ellipse icon.
- Select Stats.
- Toggle the desired measurements.
- Click Accept.
How did we do?
Chill Hours
Create a Model